Medium
Given the head of a singly linked list and two integers left and right where left <= right, reverse the nodes of the list from position left to position right, and return the reversed list.
Example 1:
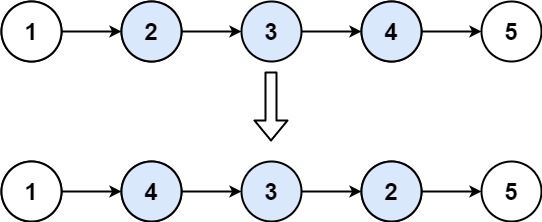
Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], left = 2, right = 4 Output: [1,4,3,2,5]
Example 2:
Input: head = [5], left = 1, right = 1 Output: [5]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the list is
n. 1 <= n <= 500-500 <= Node.val <= 5001 <= left <= right <= n
Follow up: Could you do it in one pass?
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def reverse(self, head, left, right):
prev = None
current = head
while left <= right:
temp = current.next
current.next = prev
prev = current
current = temp
left+=1
return prev, head, current
def reverseBetween(self, head: Optional[ListNode], left: int, right: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
s_head = ListNode(0, head)
i = 1
current = s_head
while i < left:
current = current.next
i+=1
#print(current.next.val)
new_head, new_tail, tail_next = self.reverse(current.next, left, right)
current.next = new_head
new_tail.next = tail_next
return s_head.next
# def reverse(self, head, left, right): # 5, 1, 2
# prev = None
# current = head # 5
# while left <= right:
# temp = current.next # 6 # None
# current.next = prev # 5.next > None | # 6.next > 5
# prev = current # 5 # 6
# current = temp # 6 # none
# left+=1 # 6 # 7
# return prev, head, current # 6 , 5, None
# def reverseBetween(self, head: Optional[ListNode], left: int, right: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
# if not head or left == right:
# return head
# current = head #(3)
# i = 1
# while i < left-1:
# if current.next:
# current = current.next #2, 2 > 3, 3 > 4, 4 >
# else:
# break
# if not current.next:
# return head
# starting_head = current # 3
# if left == 1:
# new_head, new_tail, tail_next = self.reverse(current, left, right) # 3.next > 5
# new_tail.next = tail_next
# return new_head
# else:
# new_head, new_tail, tail_next = self.reverse(current.next, left, right) # 3.next > 5
# # 6 , 5, None
# starting_head.next = new_head # 4 > 6
# new_tail.next = tail_next # 5>None
# # 1, 2, 3, 4, > 6 > 5> None
# return head
# # left -> head
# # right -> tail
# # startting_head = 1
# # end_tail = 5
# # old_head = 2
# # old_tail = 4
# # 4 > 3> 2
# # startting_head(1) > new_head = 4
# # new_tail = 2
# # new_tail (2) > end_tail
# # Revese (head (2))
# # ----------
# # prev = None
# # current = head (2)
# # left =
# # while left<=right:
# # temp(3) = current(2).next
# # current(2).next = prev (None)
# # #temp.next = current (2)
# # #prev = current (2)
# # prev (2) = current
# # current(3) = temp (3)
# # left(3) +=1
# # return prev, head
# # ------------------
# # temp(4) = current(3).next
# # current(3).next = prev (2)
# # prev (3) = current
# # current(4) = temp (4)
# # left(4) +=1
# # ------------------
# # temp(5) = current(4).next
# # current(3).next = prev (2)
# # prev (3) = current
# # current(4) = temp (4)
# # left(5) +=1